Mower Blade Balancing
Unbalance Educational Bulletin
What is unbalance?
Too much unbalance causes damaging vibration when the blade is at its operating speed. The following diagrams and information will provide the basics of understanding unbalance so that you may better service your lawn mower blades
ROTATION CENTER versus MASS CENTER
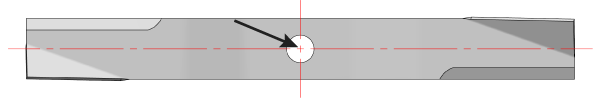
ROTATION CENTER (center of rotation) is the lawn mower blade's center of rotary motion. The rotation center is shown in the image below at the center of the cross-hair.
MASS CENTER (center of mass) is the middle point where all the weight of the blade is concentrated. It represents the unique point in a body that describes its response to external forces and torques. Steel is not evenly distributed,
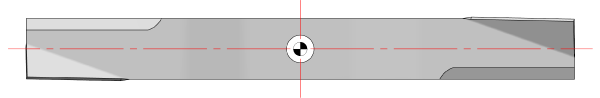
machining and sharpening are not 100% consistent, therefore the mass center and rotation center are rarely in the same place. The universal symbol for a “mass center location” is a circle with two filled opposing quarters, as shown below.
![]()
If the mass center and the rotation center are in the same place (as shown below) the blade below is statically in-balance.
Unbalance Units of Measure
If a blade has an unbalance moment of 3 ozin it means that there are three ounces of weight one inch away from the rotation center. For example “ounce inch” is a measure of torque just like “foot pounds” or (lbft), when using a torque wrench. When unbalance is calculated the unit of measure is “ounce inch” (displayed mathematically as ozin). In the metric system it is “gram millimeter” (displayed mathematically as gmm).
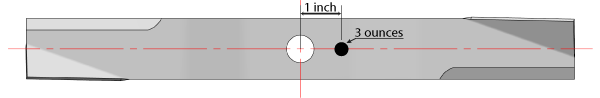
What is Horizontal Unbalance?
This blade is a larger view of a horizontal unbalance condition.
This is most often caused by inconsistent wear and sharpening.
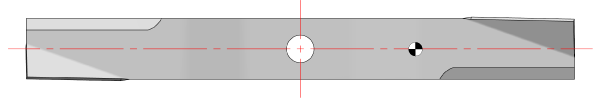
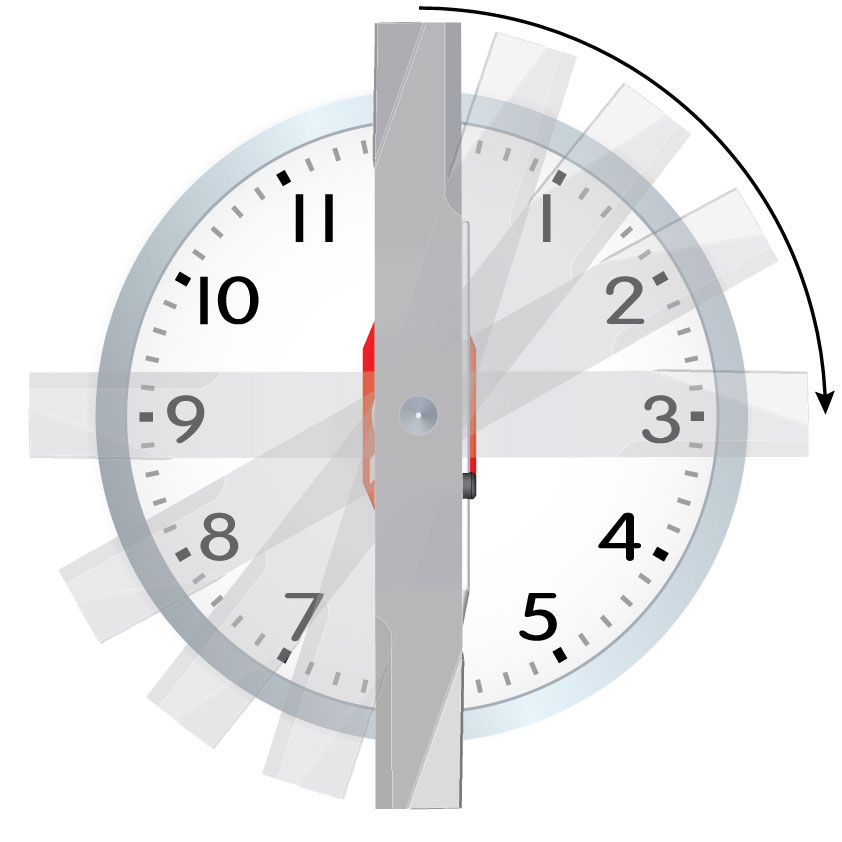
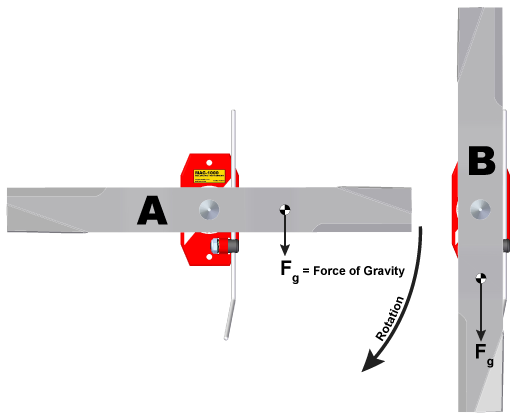
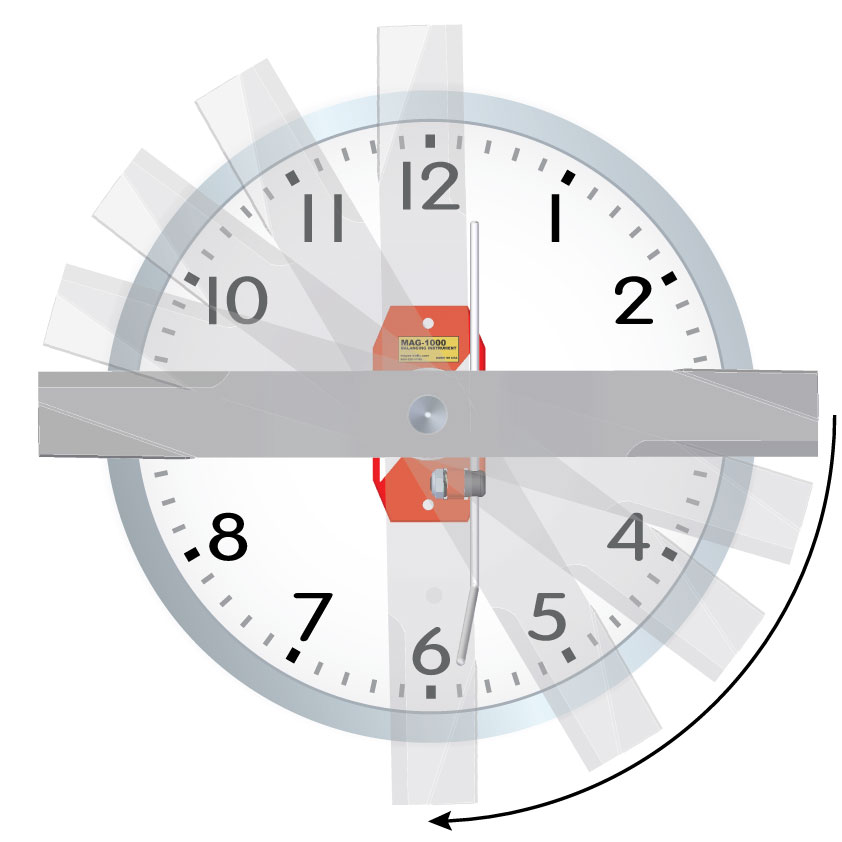
The above blade shows the mass center symbol to the right of the rotation center. Image “A” shows this blade on the MAG-1000 in the horizontal position with the mass center to the right of the rotation center. This condition will cause the right-side (heavy side) to rotate clockwise and come to rest as shown in image “B.” The mass center could be to the left of the rotation center which would cause it to rotate counter-clockwise.
A = Start position (horizontal) (3 o’clock and 9 o’clock)
B = Rest position (vertical) (12 o’clock and 6 o’clock)
What is Vertical Unbalance?
This blade is a larger view of a vertical unbalance condition.
This is most often caused when the mounting hole is not stamped in the center of the blade.
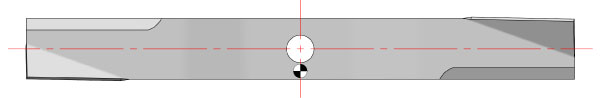
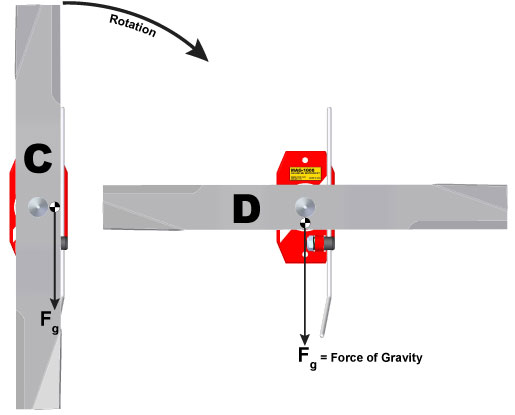
The above blade shows the mass center symbol below of the rotation center. Image “C” shows the blade on the MAG-1000 in the vertical position with the mass center to the right of the rotation center. This condition will cause the right-side (heavy side) to rotate clockwise and come to rest as shown in image “D.” The mass center could be to the left of the rotation center which would cause it to rotate counter-clockwise.
C = Start position (vertical) (12 o’clock and 6 o’clock)
D = Rest position (horizontal) (3 o’clock and 9 o’clock)